- (770) 949-5600
- info@example.com
- 6740 Douglas Blvd A Douglasville, GA 30135
CONTACT US
- (770) 949-5600
- 4128 Franklin St, California(CA), 95350
- sirpi@example.com
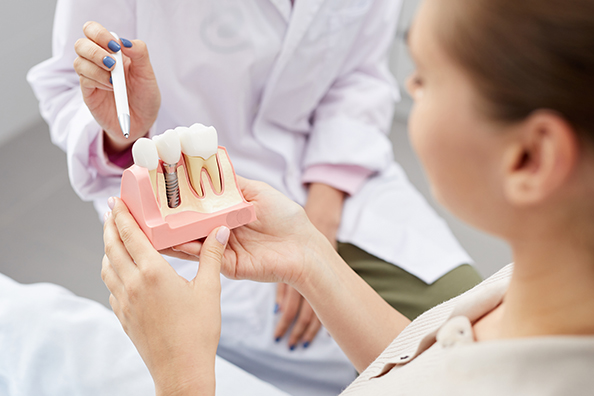
DENTAL IMPLANTS
A dental implant is a long-term, durable solution for a missing tooth. Unlike dentures, which are removable, implants are surgically anchored to the jawbone, offering unmatched stability and a natural feel. Implants can also be combined with bridges to replace multiple missing teeth, creating a seamless, noninvasive restoration. By fusing with the bone, dental implants not only restore your smile but also preserve bone density, promoting long-term oral health and function.
Frequently Asked Questions
Losing a tooth can significantly alter your appearance, especially if it’s in the front of your mouth. Missing teeth can cause the lips to lose support, leading to a sunken look. Additionally, losing molars can lead to bite collapse, pushing the front teeth forward.
Losing a tooth can harm self-confidence, leading to people hiding their smiles or avoiding social interactions. This may cause feelings of isolation and, in some cases, contribute to depression-like symptoms.
Losing a tooth can weaken neighboring teeth, which depend on each other for support. It may also lead to bone loss in the jaw over time. Dental implants help prevent this by stimulating and preserving the bone.
There are two main types: endosteal implants, which are surgically placed into the jawbone, and subperiosteal implants, which involve placing a metal frame below the gum line. Both types support crowns or bridges for tooth replacement.
To maintain dental implants, it’s essential to visit your dentist regularly, brush and floss daily, avoid hard foods that could damage crowns, and refrain from smoking, which can weaken the jawbone and affect implant longevity.